Have you ever wondered what happens to solid substances when they are subjected to heat? The transformation from solid to liquid is a fascinating process that occurs all around us. It can be seen in everyday life, from the melting of ice cubes in a refreshing drink to the way chocolate melts in your hands. Understanding how and why materials turn to liquid can deepen our appreciation for the science that governs our environment. As we explore the concept of phase changes, particularly the transition from solid to liquid, we will uncover the principles that dictate this transformation. From the molecular dynamics to the practical implications in our daily lives, the phenomenon of turning to liquid is both captivating and essential. In this article, we will investigate the factors influencing this process and the myriad of scenarios where it comes into play.
The process of solid substances turning to liquid, known as melting, is not just limited to ice or chocolate; it encompasses a wide range of materials. This transformation is primarily influenced by temperature, pressure, and the unique properties of the substance in question. By examining these factors, we can gain insight into the broader implications of phase changes and their significance in various fields, from cooking to industrial manufacturing. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the science behind melting and explore the real-world applications of these principles.
As we embark on this exploration of the melting process, we will consider several questions that arise. How do temperature and pressure affect the melting point of different materials? What are the practical applications of understanding how substances turn to liquid? And how can we observe these changes in our everyday lives? Join us as we unravel the complexities of materials that turn to liquid and discover the fascinating world of phase transitions.
What is the Science Behind Turning to Liquid?
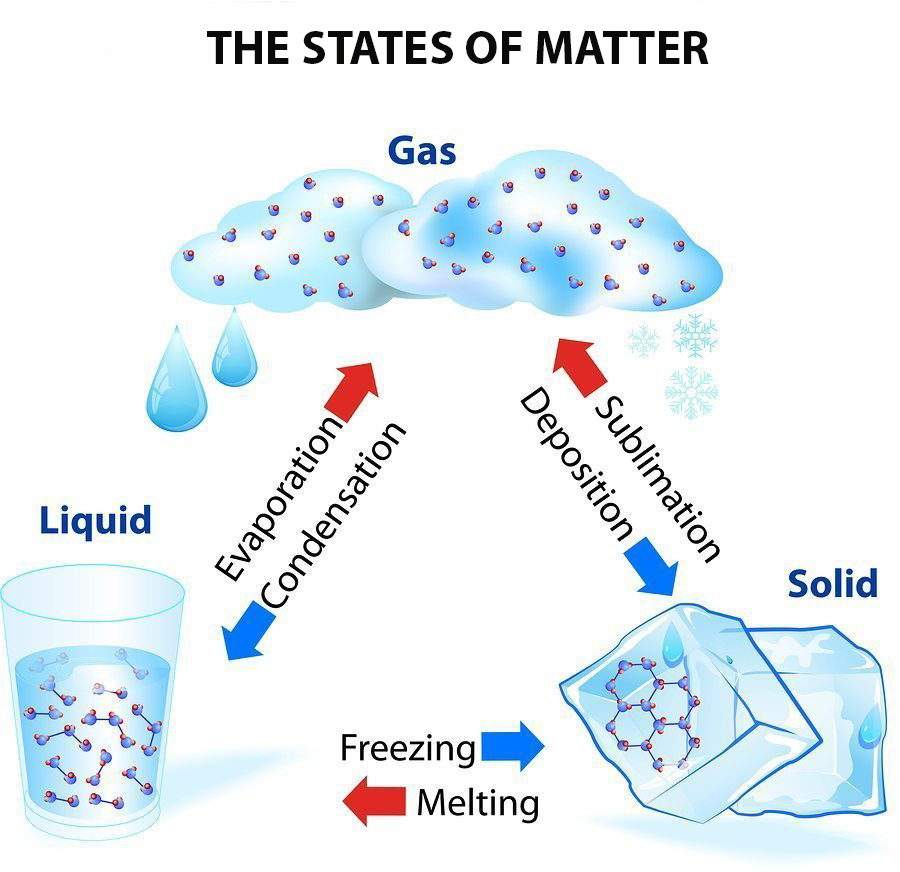
The science of turning to liquid is rooted in thermodynamics, a branch of physics that studies heat and temperature and their relation to energy and work. When a solid heats up, its particles begin to vibrate more vigorously. Once the temperature reaches a certain threshold known as the melting point, the forces holding the particles in their fixed positions begin to weaken. As a result, the solid transitions into a liquid state, where the particles can move freely but are still in close proximity to one another.
What Factors Influence the Melting Process?
Several key factors influence whether a solid will turn to liquid, including:
- Temperature: The most significant factor, as increasing temperature generally leads to melting.
- Pressure: Changes in pressure can also affect the melting point. For example, increasing pressure can raise the melting point of some substances.
- Material Properties: Different materials have varying melting points due to their molecular structure and bonding.
How Do Different Materials Behave When They Turn to Liquid?
Not all materials behave the same way when they melt. For instance:
- Ice: Melts at 0°C (32°F) under standard atmospheric pressure.
- Chocolate: Begins to melt at around 30°C (86°F) due to its fat content.
- Metals: Each metal has its unique melting point; for example, aluminum melts at about 660°C (1220°F).
Can We Observe the Melting Process in Everyday Life?
Yes! The melting process is easily observable in daily life. Here are some common examples:
- Ice cubes melting in a drink on a hot day.
- Butter melting in a skillet while cooking.
- Wax from a candle dripping as it burns.
What Are the Practical Applications of Understanding Melting?
Understanding the melting process has several practical applications, including:
- Culinary Arts: Chefs utilize melting techniques to create delicious dishes.
- Manufacturing: Industries rely on melting for processes like metal casting and plastic molding.
- Material Science: Researchers study melting points to develop new materials with specific properties.
How Does Climate Change Affect Melting Substances?
Climate change has significant implications for melting substances, particularly ice. As global temperatures rise, glaciers and polar ice caps are melting at an alarming rate. This not only contributes to rising sea levels but also impacts ecosystems and weather patterns. Understanding the melting process in this context is crucial for addressing environmental challenges.
Can We Control the Melting Process?
Yes, in many cases, we can control the melting process through techniques such as:
- Temperature Regulation: Carefully managing heat can help achieve desired melting outcomes.
- Pressure Application: In industrial settings, altering pressure can change the melting points of materials.
- Ingredient Selection: In cooking, choosing the right combination of ingredients can affect how and when melting occurs.
Are There Any Interesting Facts About Melting?
Indeed, here are some intriguing facts about melting:
- The melting point of ice decreases under pressure, a phenomenon known as regelation.
- Some substances, such as gallium, can melt in your hand at room temperature.
- Not all solids melt in a predictable manner; some, like glass, undergo a gradual transition without a defined melting point.
Conclusion: Why Is It Important to Understand the Process of Turning to Liquid?
Understanding the process of turning to liquid is fundamental for numerous fields, from environmental science to culinary arts. By grasping the principles behind melting and the factors that influence it, we can make more informed decisions in our daily lives and contribute to solving larger societal issues. Whether it's enjoying a warm chocolate dessert or addressing climate change, the ability of materials to turn to liquid plays a crucial role in our world.
Article Recommendations
- How Many Ounces Is 17 Liters
- Sons Of Noah
- Bela Rajput
- Fleur Cates Netanyahu
- Bru And Anna Sitar
- Orlando Brown Houston Tx
- Mindy Mccready Sons Today 2024
- Who Is Vince Prokop
- Down South Music
- Camilla Araujo
Also Read