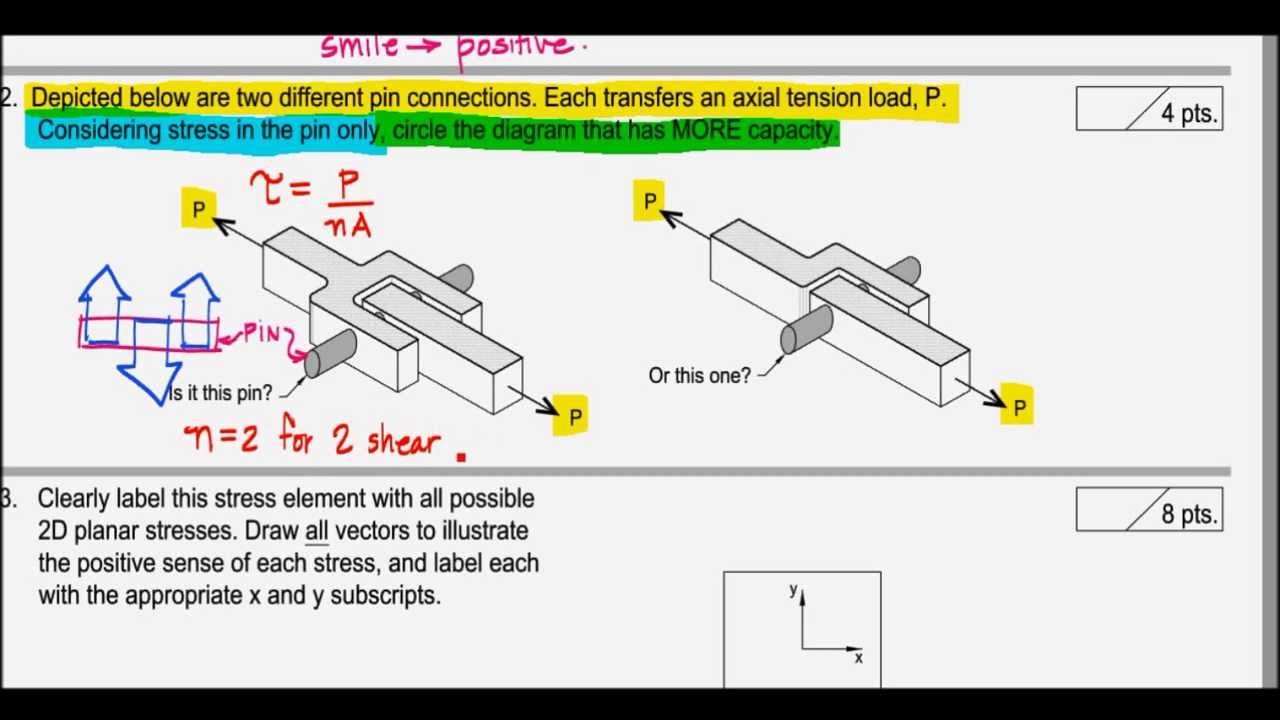
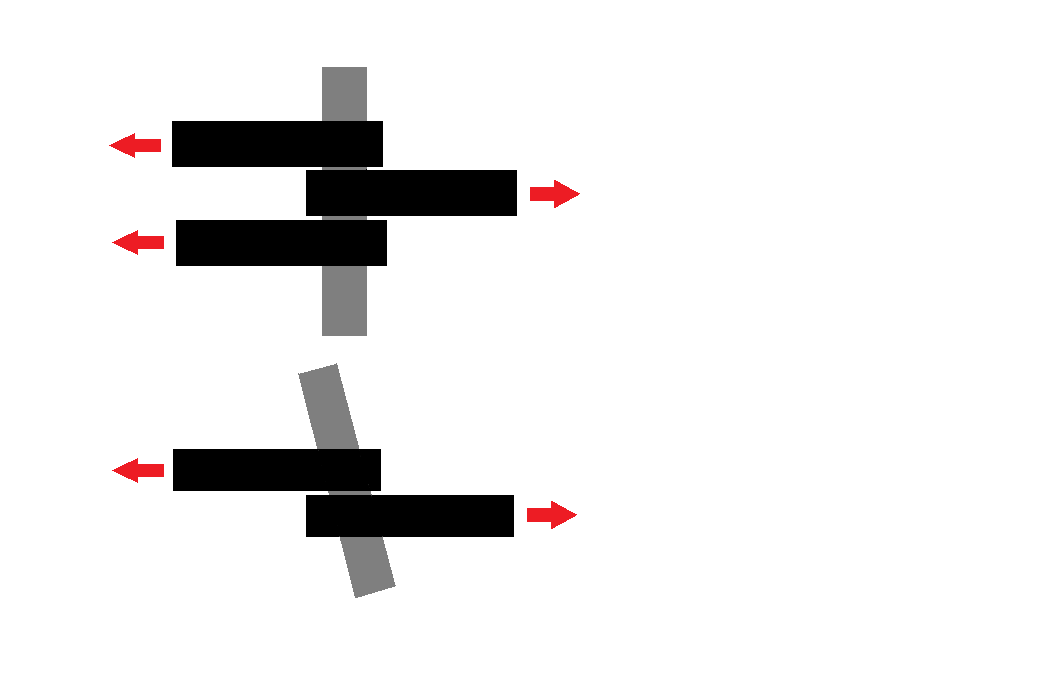
When it comes to mechanical engineering and structural applications, understanding the concepts of single shear and double shear is crucial. These terms relate to how materials behave under load, which can significantly influence the design and safety of structures. By comprehending the differences between these two types of shear, engineers can make informed decisions that ultimately lead to safer and more efficient designs.
Shear forces occur when a material experiences parallel forces in opposite directions, leading to a slippage or deformation. In the context of single shear and double shear, these forces can affect the overall integrity of components like beams, bolts, and joints. The distinction between single and double shear is not merely academic; it has practical implications for the load-bearing capacity of materials and the overall safety of structures.
In this article, we will delve into the fundamental differences between single shear and double shear, explore their real-world applications, and discuss why these concepts matter for engineers and designers. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply a curious reader, understanding single shear vs double shear will enhance your grasp of material mechanics and structural integrity.
What is Single Shear?
Single shear occurs when two forces are applied in opposite directions on a single plane, leading to a shear force that acts on a material. This type of shear is typically seen in simple connections, such as bolts or rivets, where the material can be considered to have a single layer of resistance against the applied load.
What are the Characteristics of Single Shear?
- Involves one plane of shear.
- Commonly found in simple mechanical connections.
- Generally has lower load-bearing capacity compared to double shear.
- More susceptible to failure under high loads.
What is Double Shear?
In contrast, double shear occurs when a material is subjected to shear forces on two planes. This configuration effectively distributes the load over a larger area, making double shear connections more robust and capable of withstanding greater forces than their single shear counterparts.
What are the Characteristics of Double Shear?
- Involves two planes of shear.
- Provides greater strength and load-bearing capacity.
- Commonly used in applications requiring enhanced durability.
- Less prone to failure under high loads compared to single shear.
How Do Single Shear and Double Shear Compare?
To better understand the differences between single shear and double shear, it is helpful to compare their respective characteristics side by side:
| Feature | Single Shear | Double Shear |
|---|---|---|
| Planes of Shear | 1 | 2 |
| Load-Bearing Capacity | Lower | Higher |
| Common Applications | Simple connections (e.g., bolts) | Heavy machinery, structural components |
| Susceptibility to Failure | Higher under load | Lower under load |
What are the Applications of Single Shear?
Single shear is often utilized in various applications where the loads are relatively light and do not require extensive strength. Some common uses include:
- Simple fastening methods like screws and bolts.
- Riveted joints in low-load structures.
- Applications in furniture and light machinery.
What are the Applications of Double Shear?
Double shear is preferred in applications where higher strength and durability are necessary. Examples include:
- Heavy machinery and equipment.
- Structural components in buildings and bridges.
- Automotive and aerospace applications.
Why is Understanding Single Shear vs Double Shear Important?
Understanding the differences between single shear and double shear is vital for engineers and designers as it influences material selection, design specifications, and safety considerations. Choosing the appropriate type of shear for a given application can prevent catastrophic failures and ensure the longevity of structures. Furthermore, this knowledge aids in optimizing costs by selecting materials and designs that meet the required performance criteria without over-engineering components.
How to Perform Shear Strength Calculations?
Calculating shear strength involves understanding the material properties and the configuration of the shear. Here are the steps to perform basic shear strength calculations:
- Determine the shear area: For single shear, this is the cross-sectional area of the bolt or rivet. For double shear, it is double the cross-sectional area.
- Find the material's shear strength: This can often be found in material property tables.
- Use the formula: Shear strength = Shear area x Shear strength of the material.
By understanding and applying these principles, designers can ensure the effective use of materials and create structures that can withstand the forces they will encounter throughout their service life.
Article Recommendations
- Eric Slovin Net Worth
- Kunefe
- Timothy Bass Murder
- Celebrities Black Eye
- How Many Ounces Is 17 Liters
- Full Potential
- Woo Lotti Video
- Huberman Wife
- Sean Preston Federline 2024
- Fleur Cates Netanyahu
Also Read