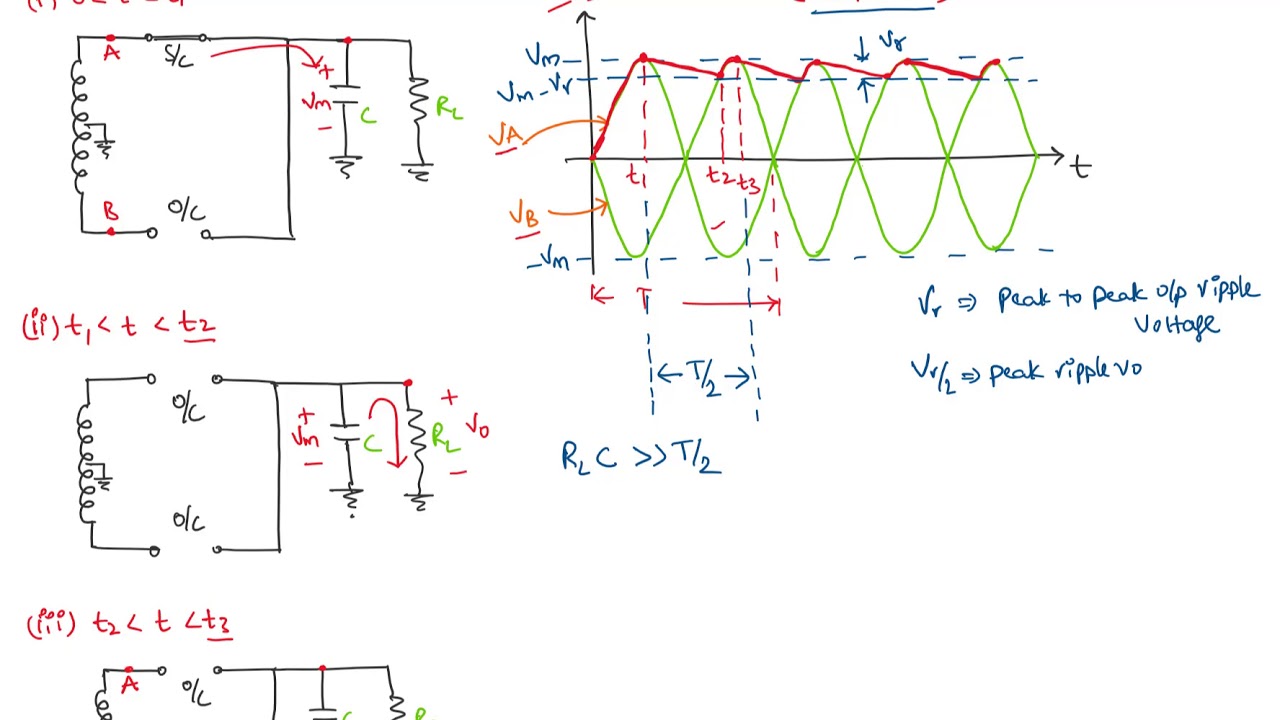
The full wave rectifier with capacitor filter is a crucial device in the world of electronics, widely used for converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). This transformation is essential for powering various electronic circuits and devices, ensuring they function efficiently and reliably. By employing a full wave rectifier, engineers can maximize the output voltage and achieve a smoother DC signal by utilizing a capacitor filter, which smooths out the ripples inherent in rectified DC voltage.
In the realm of power supply design, the full wave rectifier with capacitor filter stands out as a preferred choice due to its ability to provide a more stable and efficient output compared to half-wave rectifiers. This article delves into the working principles, advantages, and applications of this powerful configuration, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance in electronic circuits.
As we explore the intricacies of the full wave rectifier with capacitor filter, we will address common questions, such as how it operates, what components are involved, and why it is favored over other rectification methods. Additionally, we will discuss practical applications and considerations for implementing this technology in various electronic designs.
What is a Full Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter?
A full wave rectifier with capacitor filter is essentially a circuit that converts both halves of an AC waveform into a usable DC output. This configuration employs a full wave rectifier, which can be built using either a center-tapped transformer or a bridge rectifier arrangement. The primary function of the capacitor filter is to smooth out the resulting pulsating DC voltage, resulting in a more stable and continuous output.
How Does a Full Wave Rectifier Work?
The operation of a full wave rectifier can be better understood by examining its components and the process involved in rectification. Here’s a breakdown of the working mechanism:
- The AC input is fed into the rectifier circuit, where it is transformed into a pulsating DC signal.
- During both positive and negative cycles of the AC input, the rectifier allows current to flow through, effectively utilizing both halves of the waveform.
- The capacitor filter then comes into play, storing charge during the peaks of the pulsating DC voltage and releasing it during the troughs, thus smoothing out the output voltage.
What Are the Components of a Full Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter?
To construct a full wave rectifier with capacitor filter, several key components are required:
- Rectifier Diodes: Typically, four diodes are used in a bridge configuration.
- Capacitor: This stores and smooths the rectified voltage.
- Transformer: If a center-tapped rectifier is used, a transformer is necessary to step down the voltage.
- Load Resistor: This represents the device being powered by the rectified output.
What Are the Advantages of Using a Full Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter?
The full wave rectifier with capacitor filter offers several notable advantages, making it a popular choice in electronic applications:
- Higher Efficiency: It utilizes both halves of the AC waveform, resulting in a higher average output voltage.
- Improved Ripple Voltage: The capacitor filter significantly reduces the ripple voltage, leading to a more stable DC output.
- Smaller Filter Size: Compared to half-wave rectifiers, the size of the filter capacitor can be smaller due to the reduced ripple.
What Are the Applications of Full Wave Rectifiers with Capacitor Filters?
Full wave rectifiers with capacitor filters find applications in various fields, including:
- Power supply units for electronic devices
- Battery chargers
- DC motor drives
- Audio amplifiers
What Considerations Should Be Made When Designing a Full Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter?
When designing a full wave rectifier with capacitor filter, several factors should be considered:
- Voltage Rating: Ensure that all components, especially diodes and capacitors, can handle the maximum voltage.
- Capacitance Value: Choose an appropriate capacitance value based on the desired ripple voltage and load current.
- Heat Dissipation: Diodes can generate heat during operation, so adequate heat sinking may be necessary.
How to Calculate the Output Voltage of a Full Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter?
The output voltage of a full wave rectifier can be calculated using the following formula:
VDC = Vpeak - Vdrop
Where:
- VDC: The average DC output voltage
- Vpeak: The peak voltage of the AC input
- Vdrop: The forward voltage drop across the diodes (typically around 0.7V per diode)
Conclusion: Why Choose a Full Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter?
In conclusion, the full wave rectifier with capacitor filter is an indispensable component in the design of efficient and stable DC power supplies. By effectively converting AC to DC and smoothing out the voltage fluctuations, this configuration ensures that electronic devices operate smoothly and reliably. Its numerous advantages, including higher efficiency and reduced ripple voltage, make it a preferred choice among engineers and designers alike.
Article Recommendations
- Sons Of Noah
- Afghanistan Language
- Esther Rolle Children
- Bru And Anna Sitar
- Third Eye Blind Songs
- How To Clear An External Hard Drive
- Actors Superbad
- Burning House
- Brad Pitt Height
- Beyonce Breakup
Also Read