Statistical analysis plays a vital role in understanding data and making informed decisions. Among the myriad of concepts in statistics, variance is one of the most crucial. It serves as a measurement of how spread out the numbers in a data set are. When analyzing data, one must consider whether the variance is equal or unequal across different groups, as this can significantly impact the results of tests and the conclusions drawn from them. The distinction between unequal vs equal variance is not merely academic; it has real-world implications in fields such as psychology, medicine, and social sciences.
The concept of variance is essential for conducting various statistical tests, including t-tests and ANOVA (Analysis of Variance). Knowing whether the variances of the groups being compared are equal or unequal can determine the appropriate statistical methods to use. If the variances are unequal, using standard statistical tests that assume equal variance may lead to incorrect conclusions. Thus, understanding the implications of unequal vs equal variance is critical for anyone involved in data analysis.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the differences between unequal and equal variance, exploring their definitions, how to test for them, and the implications of each. We will also answer common questions about the topic and provide guidance on how to handle situations involving unequal vs equal variance in practical applications. By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of these vital concepts in statistics.
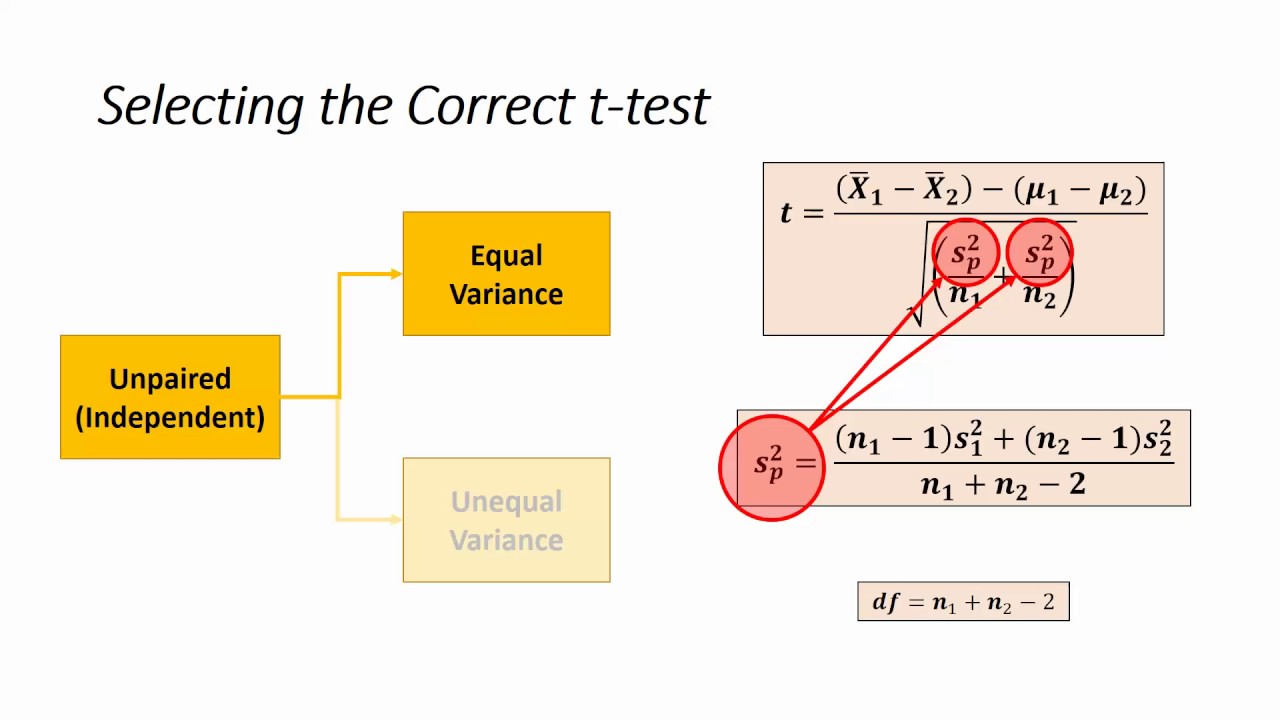
What is Equal Variance?
Equal variance, also known as homogeneity of variance, refers to a situation where two or more groups in a statistical analysis have the same variance. This assumption is critical for many statistical tests, especially t-tests and ANOVA, which rely on the premise that the variances of the groups being compared are equal. When this assumption holds true, the results of the statistical tests are more reliable and valid.
How is Equal Variance Tested?
Several statistical tests can be employed to determine whether variances are equal across groups. Some of the most commonly used tests include:
- Levene's Test: This test assesses the equality of variances by analyzing the absolute deviations of each observation from the group mean. It is robust to departures from normality.
- Brown-Forsythe Test: Similar to Levene's Test, this method uses the median instead of the mean, making it less sensitive to outliers.
- F-test: This test compares the variances of two groups directly. However, it is sensitive to violations of normality and should be used with caution.
What is Unequal Variance?
Unequal variance, or heteroscedasticity, occurs when the variances of different groups in a statistical analysis are not the same. This situation can lead to challenges in statistical testing, as many tests assume equal variances. When variances are unequal, the results may be biased, and the validity of the conclusions drawn from the data can be compromised.
How Does Unequal Variance Affect Statistical Tests?
When conducting statistical tests with unequal variances, researchers must be cautious. Using standard t-tests or ANOVA when the equal variance assumption is violated can lead to:
- Increased Type I Error Rate: This is the probability of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true.
- Reduced Power: The ability of a test to detect an effect when there is one may decrease.
- Misleading Results: Conclusions drawn from the analysis may be incorrect, leading to poor decision-making.
How to Handle Unequal Variance?
When faced with unequal variance, researchers have several options to ensure their analysis remains valid:
- Use Alternative Statistical Tests: Tests such as Welch's t-test or the Brown-Forsythe ANOVA do not assume equal variances and can provide more reliable results.
- Transform the Data: Sometimes, applying a transformation (like a logarithmic or square root transformation) can help stabilize variances.
- Consider Non-parametric Tests: Non-parametric tests, which do not rely on assumptions about variance, can be an excellent alternative.
What Are the Practical Implications of Unequal vs Equal Variance?
Understanding the difference between unequal and equal variance is crucial for researchers and analysts. The choice of statistical tests and methods can significantly impact the conclusions drawn from data. Here are some practical implications:
- In Research: Accurate handling of variance ensures that findings are valid and can be generalized to larger populations.
- In Business: Businesses rely on data analysis for decision-making. Misinterpretation due to variance issues can lead to poor strategic choices.
- In Policy Making: Policymakers must base their decisions on sound data. Ignoring variance can result in policies that do not effectively address the issues at hand.
How to Report Findings with Unequal vs Equal Variance?
When reporting findings from statistical analyses, it is essential to clearly state whether equal or unequal variance was assumed. This transparency helps others understand the context of the results and their implications. Key points to include in reports are:
- Statistical Tests Used: Clearly state which tests were conducted and whether they assumed equal or unequal variance.
- Results of Variance Tests: Include the results of any tests conducted to assess variance equality, such as Levene's Test.
- Implications of Findings: Discuss how the variance impacted the conclusions drawn from the analysis.
Conclusion: Why is Understanding Variance Important?
In summary, the distinction between unequal vs equal variance is a fundamental aspect of statistical analysis that can influence the outcome of research and data interpretation. It is crucial for researchers to understand these concepts, test for variance equality, and choose appropriate statistical methods. By doing so, they can ensure that their analyses are valid, their conclusions are reliable, and their findings can contribute meaningfully to their respective fields.
Article Recommendations
- Joe Metheny
- Abel Tesfaye Selena Gomez
- Sandy Playboy
- Kim Scott Mathers Today
- David Lee Rothaughter
- Keith Washington Singer
- Pax Thien Jolie Pitt Wikipedia
- Zodiac Signs June 8th
- Burning House
- Dti Reality Television Theme
Also Read